Thursday, May 17, 2012
SRM 156 DIV 2 250
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class DiskSpace
{
public int minDrives(int[] used, int[] total)
{
int n= used.length;
int t=0;
ArrayList<Integer> l=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
l.add(total[i]);
Collections.sort(l);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
t+=used[i];
}
int c=0;
System.out.println(t);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
System.out.println("-"+l.get(n-i-1));
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--,c++)
{
t-=l.get(i);
if(t<=0)break;
}
return c+1;
}
<%:testing-code%>
}
//Powered by [KawigiEdit] 2.0!
SRM 154 DIV-2 450
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class SuperRot
{
public String cd="ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789 ";
public String dc="NOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklm5678901234 ";
public String decoder(String message)
{
String r="";
for(int i=0;i<message.length();i++)
{
r+=dc.charAt(cd.indexOf(message.charAt(i)));
}
return r;
}
<%:testing-code%>
}
//Powered by [KawigiEdit] 2.0!
SRM 153 DIV1 - 250
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class Inventory
{
public int monthlyOrder(int[] sales, int[] daysAvailable)
{
double p=0;
double d=0;
double s=0;
double c=0;
for(int i=0;i<sales.length;i++)
{
if(sales[i]>0)
{
p=sales[i];
d=daysAvailable[i];
s+=(p*30/d);
c+=1.0f;
System.out.println((p*30/d));
System.out.println(s);
}
}
System.out.println(s/c);
System.out.println(Math.floor((s/c)*10e9)/10e9);
return (int)Math.ceil((Math.floor((s/c)*10e9))/10e9);
}
}
//Powered by [KawigiEdit] 2.0!
SRM 152 DIV1 - 500
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class QuiningTopCoder
{
public class Stk
{
public long st[]=null;
public int si=-1;
public boolean overflow=false;
public Stk(int lm)
{
st=new long[lm];
}
public void push(long s)
{
st[++si]=s;
if(s<-1000000000l||s>1000000000l)overflow=true;
}
public long pop()
{
long s=0;
if(si>=0)s=st[si];
si--;if(si<0)si=-1;
return s;
}
public void prt()
{
if(si<0)System.out.println("Empty");
for(int i=0;i<=si;i++)
{
if(i>0)System.out.print(",");
System.out.print(st[i]);
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
public String testCode(String source)
{
int ip=0;
long d=1;
long dd=1;
int n=source.length();
int c=0;
int lm=80000;
Stk st=new Stk(lm*2+1);
String pp=new String();
while(c<lm)
{
char a=source.charAt(ip);
dd=1;
if(a>='0'&&a<='9')
{
st.push((long)(a-'0'));
}
else if(a=='$')
{
st.pop();
}
else if(a==':')
{
long s=st.pop();
st.push(s);
st.push(s);
}
else if(a=='W')
{
long s1=st.pop();
long s2=st.pop();
st.push(s1);
st.push(s2);
}
else if(a==',')
{
long s=st.pop();
pp+=source.charAt((int)(Math.abs(s)%n));
}
else if(a=='+')
{
long s1=st.pop();
long s2=st.pop();
st.push(s1+s2);
}
else if(a=='-')
{
long s1=st.pop();
long s2=st.pop();
st.push(s1-s2);
}
else if(a=='#')
{
dd=2;
}
else if(a=='R')
{
d*=-1;
}
else if(a=='S')
{
long s1=st.pop();
st.push(s1>0?1:-1);
}
else if(a=='_')
{
long s1=st.pop();
d=s1%n;
}
else if(a=='J')
{
long s1=st.pop();
ip=(int)(Math.abs(s1)%n);
}
else if(a=='@')
break;
//if(c>0)
//{
// System.out.println("c="+c+",a="+a+",pp="+pp);
// st.prt();
//}
if(st.overflow)return "OVERFLOW "+c;
if(pp.length()==n)if(pp.equals(source))return "QUINES "+c;
if(source.indexOf(pp)!=0)return "MISMATCH "+c;
c++;
if(a!='J')
ip=(int)((ip+d*dd+3*n)%n);
}
if(c>=lm)return "TIMEOUT";
System.out.println("pp:"+pp);
return "BADEND "+c;
}
}
//Powered by [KawigiEdit] 2.0!
Tuesday, May 15, 2012
SRM 150 DIV1 - 250
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class InterestingDigits
{
private int newsum(int n,int b)
{
int s=0;
while(n!=0)
{
s+=n%b;
n=n/b;
}
return s;
}
public int[] digits(int base)
{
int m=1;
int r[]=new int[base];
int ri=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
m*=base;
for(int p=2;p<base;p++)
{
boolean pass=true;
for(int i=0;i<m;i+=p)
{
if((newsum(i,base)%p)!=0)pass=false;
}
if(pass)r[ri++]=p;
}
int r2[]=new int[ri];
for(int i=0;i<ri;i++)
r2[i]=r[i];
return r2;
}
}
Saturday, April 7, 2012
Create Android App with AndEngine.
1. Download and install latest MotoDev (3.1) for Android
2. Install latest ADK(4.0.3) and ADK tools (r17) from google site
3. Download AndEngine (4/7/2012) + Extensions Source code
4. Import those folders with source code to MotoDev
4. Makes sure AndEngineExamples have the following projects as libraries in Android property
5. And every extensions must have AndEngine as libraries.
6. Project-->Build All
7. Connect your cell phone thru USB.
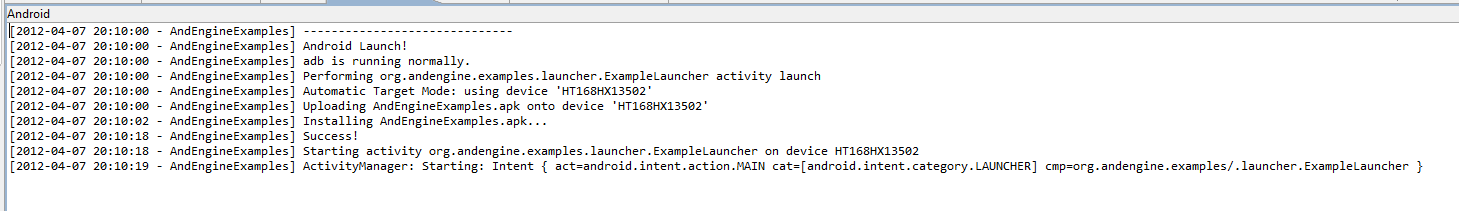
8. In Project Explorer, right click on AndroidExample, select Run as --> Android Application
After a while, you will see AndEngine demo program running.
9. In case you cannot debug your app in your cell phone, try copy dx.jar to the platform-tools\lib\ folder and do step 8 again.
From : android-sdk\platforms\android-4\tools\lib\jx.jar
To: android-sdk\platform-tools\lib\dx.jar
2. Install latest ADK(4.0.3) and ADK tools (r17) from google site
- In MotoDev-->help-->Install new software. Type ' https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/' in work with field and Add.
- Follow the steps shown on computer to get the latest ADK and tools.
3. Download AndEngine (4/7/2012) + Extensions Source code
4. Import those folders with source code to MotoDev
4. Makes sure AndEngineExamples have the following projects as libraries in Android property
5. And every extensions must have AndEngine as libraries.
6. Project-->Build All
7. Connect your cell phone thru USB.
8. In Project Explorer, right click on AndroidExample, select Run as --> Android Application
After a while, you will see AndEngine demo program running.
9. In case you cannot debug your app in your cell phone, try copy dx.jar to the platform-tools\lib\ folder and do step 8 again.
From : android-sdk\platforms\android-4\tools\lib\jx.jar
To: android-sdk\platform-tools\lib\dx.jar
Sunday, March 11, 2012
My solution of UVA 10858 - Unique Factorizatio
10858 - Unique Factorizatio
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define forr(i,b) for(int i=0;i<b;i++)
using namespace std;
#define NN 2000000
stringstream ss;
int k;
vector<string> sd;
void rep(int n, int a, string s)
{
for(int i=a;i*i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
stringstream ss(s);
ss<<s<<i<<" ";
rep(n/i,i,ss.str());
}
}
stringstream ss(s);
ss<<s<<n<<endl;
sd.push_back(ss.str());
k++;
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int N;
k=0;
while(cin>>N)
{
if(N==0)break;
k=0;
sd.clear();
rep(N,2,"");
cout<<k-1<<endl;
forr(i,k-1)cout<<sd[i];
}
return 0;
}
Friday, March 9, 2012
Algorithm study: Josephus Problem
The survivor label = (((((0+m1%2)+m2)%3+m3)%4 +m4)%5+m5)%6....
Examples:
Player : [0..5]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3,4,5}
=>{0,1,3,4,5} - 2
=>{0,1,3,4} - 5
=>{0,1,4} - 3
=>{0,1} - 4
=>{0} - 1
Saved=(((((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4+3)%5+3)%6
= 1->1->0->3->0
Player : [0..4]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3,4}
==>{0,1,3,4} -2
==>{0,1,3} -4
==>{1,3} - 0
==>{3} - 1
Saved=((((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4+3)%5
= 1->1->0->3
Player : [0..3]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3}
==>{0,1,3} -2
==>{0,3} - 1
==>{0} - 3
Saved=(((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4
= 1->1->0
Player : [0..2]
If m=3,
{0,1,2}
==>{0,1} -2
==>{1} - 0
Saved=((0+3)%2+3)%3
= 1->1
Player : [0..1]
If m=3,
{0,1}
==>{0,1} -0
==>{1}
Saved=(0+3)%2
= 1
Player : [0]
No need to play!
Saved= 0
But, Why?
====================
Proof.
If there is n people, last killed guy is X, (X+m)%n will be the next guy to be killed.
If there is n people, killed guy is Y, (Y-m)% (n) will be the prev guy to be killed.
and all label after >= (Y-m)%(n) will be +1, then the last guy labelled as (Y-m)%n;
Ok, we do the process backward.
If the saviour guy is 0. add dummy 1.
(0-m)%2 will be the prev guy to be kill => (0-3)%2 =-3%1=1.
If we enforce prev guy to be zero, all other guys need to advance to position (?+m)%2, ?={0,1}
0->1
Then we add this new prev guy as '0'
1->0
The total displacement of the surviour = 0+m%2 = 1.
Result:{0,1}
Then in next round, added a dummy 2.
(0-m)%3 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%3=0
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%3, ?={0,1,2}
1->1
2->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
0->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = ((0+m%2)+m)%3
Result:{0,1,2}
Then in next round, added a dummy 3.
(0-m)%4 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%4=1
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%4, ?={0,1,2,3}
0->3
2->1
3->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
1->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = (((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4
Result:{0,1,2,3}
Then in next round, added a dummy 4.
(0-m)%5 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%5=2
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%5, ?={0,1,2,3,4}
0->3
1->4
3->1
4->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
2->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = ((((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4+m)%5
Result:{0,1,2,3,4}
Then in next round, added a dummy 5.
(0-m)%6 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%6=3
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%6, ?={0,1,2,3,4,5}
0->3
1->4
2->5
4->1
5->2(dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
3->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = (((((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4 +m)%5+m)%6
Result:{0,1,2,3,4,5}
* If m is changing in each round, the equation will be:
The total displacement of the surviour = (((((0+m1%2)+m2)%3+m3)%4 +m4)%5+m5)%6.....
Examples:
Player : [0..5]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3,4,5}
=>{0,1,3,4,5} - 2
=>{0,1,3,4} - 5
=>{0,1,4} - 3
=>{0,1} - 4
=>{0} - 1
Saved=(((((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4+3)%5+3)%6
= 1->1->0->3->0
Player : [0..4]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3,4}
==>{0,1,3,4} -2
==>{0,1,3} -4
==>{1,3} - 0
==>{3} - 1
Saved=((((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4+3)%5
= 1->1->0->3
Player : [0..3]
If m=3,
{0,1,2,3}
==>{0,1,3} -2
==>{0,3} - 1
==>{0} - 3
Saved=(((0+3)%2+3)%3+3)%4
= 1->1->0
Player : [0..2]
If m=3,
{0,1,2}
==>{0,1} -2
==>{1} - 0
Saved=((0+3)%2+3)%3
= 1->1
Player : [0..1]
If m=3,
{0,1}
==>{0,1} -0
==>{1}
Saved=(0+3)%2
= 1
Player : [0]
No need to play!
Saved= 0
But, Why?
====================
Proof.
If there is n people, last killed guy is X, (X+m)%n will be the next guy to be killed.
If there is n people, killed guy is Y, (Y-m)% (n) will be the prev guy to be killed.
and all label after >= (Y-m)%(n) will be +1, then the last guy labelled as (Y-m)%n;
Ok, we do the process backward.
If the saviour guy is 0. add dummy 1.
(0-m)%2 will be the prev guy to be kill => (0-3)%2 =-3%1=1.
If we enforce prev guy to be zero, all other guys need to advance to position (?+m)%2, ?={0,1}
0->1
Then we add this new prev guy as '0'
1->0
The total displacement of the surviour = 0+m%2 = 1.
Result:{0,1}
Then in next round, added a dummy 2.
(0-m)%3 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%3=0
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%3, ?={0,1,2}
1->1
2->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
0->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = ((0+m%2)+m)%3
Result:{0,1,2}
Then in next round, added a dummy 3.
(0-m)%4 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%4=1
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%4, ?={0,1,2,3}
0->3
2->1
3->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
1->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = (((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4
Result:{0,1,2,3}
Then in next round, added a dummy 4.
(0-m)%5 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%5=2
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%5, ?={0,1,2,3,4}
0->3
1->4
3->1
4->2 (dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
2->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = ((((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4+m)%5
Result:{0,1,2,3,4}
Then in next round, added a dummy 5.
(0-m)%6 will be prev guy to be killed = -3%6=3
If we let this guy to be zero, all guys need to advance to position (?+m)%6, ?={0,1,2,3,4,5}
0->3
1->4
2->5
4->1
5->2(dummy)
Then we add this new guy as '0'.
3->0;
The total displacement of the surviour = (((((0+m%2)+m)%3+m)%4 +m)%5+m)%6
Result:{0,1,2,3,4,5}
* If m is changing in each round, the equation will be:
The total displacement of the surviour = (((((0+m1%2)+m2)%3+m3)%4 +m4)%5+m5)%6.....
Labels:
Algorithm,
algorithms,
competitive,
dynamic programming,
Explaination,
Joseph,
Josephus,
Problem,
programming,
uva
Thursday, March 8, 2012
My solution of 763 - Fibinary Numbers (C++ without BigInteger)
763 - Fibinary Numbers
(WA) many times... but still don't know why. maybe missing the last linebreak.
(CE) Cannot use printf in UVAonlinejudge without #include<stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define sz(k) (int)(k).size()
#define tr(c,i) for(typeof((c).begin()) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); i++)
#define forr(i,r) for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define drep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define pb push_back
#define nl(c) c<<endl;
#define db(cout,c) tr(c,it){cout<<" "<<*it;};nl(cout);
#define inf24 (int)(1<<23-1)
#define inf32 (int)(1<<31-1)
#define inf64 (long long)(1LL<<63-1)
using namespace std;
#define NN 10240
unsigned long long fb[NN+NN+2];
int sum[(NN+NN+2)];
unsigned long long cksum1,cksum2;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//fb[0]=1;fb[1]=2;
//forr(i,NN+NN)fb[i+2]=fb[i]+fb[i+1];
int T=0,stage=1;
string S1,S2;
while(cin>>S1>>S2)
{
if(T>0)cout<<endl;
T++;
//cout<<"S1="<<S1<<endl;
//cout<<"S2="<<S2<<endl;
forr(i,NN+NN)sum[i]=0;
forr(i,S1.size())sum[S1.size()-i-1]=(S1[i]-'0');
forr(i,S2.size())sum[S2.size()-i-1]+=(S2[i]-'0');
/*
cksum1=0;
forr(i,NN+NN)cksum1+=sum[i]*fb[i];
stage=1;
drep(i,NN+NN-1,0){
if(stage==1)if(sum[i]>=1)stage=2;
if(stage==2)
cout<<sum[i];
}
cout<<" ("<<cksum1<<")";
cout<<endl;
*/
stage=1;
while(stage==1)
{
stage=2;
forr(i,NN+NN-2)
{
if(sum[i]>=1&&sum[i+1]>=1)
{
sum[i]--;
sum[i+1]--;
sum[i+2]++;
stage=1;
}
else if(sum[i]>=2&&i>1)
{
sum[i]--;
sum[i]--;
sum[i+1]++;
sum[i-2]++;
stage=1;
}
else if(sum[1]>=2)
{
sum[1]-=2;
sum[2]++;
sum[0]++;
stage=1;
}
else if(sum[0]>=2)
{
sum[0]-=2;
sum[1]++;
stage=1;
}
}
}
stage=1;
drep(i,NN+NN-1,0){
if(stage==1)
if(sum[i]>=1)stage=2;
if(stage==2)
cout<<sum[i];
}
if(stage==1)cout<<"0";
stage=2;
//cksum2=0;
//forr(i,NN+NN)cksum2+=sum[i]*fb[i];
//cout<<" ("<<cksum2<<")";
cout<<endl;
// printf("\r\n");
};
return 0;
}
Wednesday, March 7, 2012
My solution of UVA 10954 - Add All (using priority_queue)
10954 - Add All
* Similarity to Huffman coding problem.
* Solve by priority queue.
* Compare with 'min multiplication operation' - the order of the variables/martix can not be rearranged/sort.
* Add All is easier and don't need dp[][].
* On the other hand, dp can be used if the order of the variables always fixed.
* Please notice how to define <priority_queue>:
priority_queue<long long, vector<long long>, greater<long long> > l;
----- CODE -----
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define forr(i,b) for(int i=0;i<b;i++)
#define tr(c,i) for(typeof((c).begin()) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); i++)
#define nl(c) c<<endl;
#define db(cout,c) tr(c,it){cout<<*it<<",";};nl(cout);
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int N,a;
while(cin>>N)
{
if(N==0)break;
priority_queue<long long, vector<long long>, greater<long long> > l;
forr(i,N){cin>>a;l.push(a);}
long long sum=0LL;
do{
a=l.top();l.pop();
a+=l.top();l.pop();
sum+=a;
l.push(a);
}while(l.size()>1);
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
My solution of UVA 443 - Humble Numbers
443 - Humble Numbers
- Cannot use value-dp[], because 20000000000 > 32bit int and it is too large.
- Same reason, cannot use Eratosthenes Prime Number Sieve
- Notice how to generate 1st, 2nd, 111th, 221st etc... check both N%10 and N%100 (easy to miss N%100 part).
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define sz(k) (int)(k).size()
#define tr(c,i) for(typeof((c).begin()) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); i++)
#define forr(i,r) for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define drep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define pb push_back
#define nl(c) c<<endl;
#define db(cout,c) tr(c,it){cout<<" "<<*it;};nl(cout);
#define inf24 (int)(1<<23-1)
#define inf32 (int)(1<<31-1)
#define inf64 (long long)(1LL<<63-1)
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
long long h[5844];
h[1]=1LL;
long long lim=1,hi=1,min;
long long pt[]={2LL,3LL,5LL,7LL};
rep(i,1,5844)
{
min=inf64;
for(int j=i;j>=1;j--)
{
int k=0;
for(;k<4;k++)
{
long long test=h[j]*pt[k];
if(test<min&&test>lim)
{
min=test;
// cout<<j<<","<<k<<"="<<min<<endl;
}
}
if(h[j]*pt[3]<lim)break;
}
lim=h[i+1]=min;
// cout<<"h["<<i+1<<"]="<<min<<endl;
}
int N,N10,N100;
while(cin>>N)
{
if(N==0)break;
string su;
su="th";
N10=N%10;
N100=N%100;
if(N10==1&&N100!=11)su="st";
if(N10==2&&N100!=12)su="nd";
if(N10==3&&N100!=13)su="rd";
cout<<"The "<<N<<su<<" humble number is "<<h[N]<<"."<<endl;
};
return 0;
}
Tuesday, March 6, 2012
My solution UVA 264 - Count on Cantor O(1) solution
264 - Count on Cantor
Time complexity: O(1)
The change of A[i] =
1
12321
123454321
1234567654321
The label of A[i] =row r
row 1: 1,
row 2: 2,3,4,5,6,
row 3: 7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,
row 4: 16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,
row 5: 29,30,31,...45
The size of row r = 4r-3
The last item of row r:
row 1: 1
row 2: 6
row 3: 15
row 4: 28
row 5: 45
=sum(4r-3)=2r^2-r
The first item of row r:
row 1: 1
row 2: 2
row 3: 7
row 4: 16
row 5: 29
= 1+ last item of row (r-1) =2(r-1)^2-(r-1) +1 = s = 2r^2-5r+4
Given current position = N,
N>=2r^2-5r+4
2r^2-5r-(N-4)<=0
r<=(5+sqrt(25+8(N-4)))/4
r=(int)(5+sqrt(25+8(N-4)))/4
offset in row r : o = N-s
max value of row r : z=2*r-1;
We use offset and search/compute the value of A(N) in row r : A=z-abs(o-z+1);
We can find out B in the similar way.
---------------------------- CODE ---------------------------
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int N;
int A,B;
int r,t,s,o,z;
while(cin>>N)
{
t=N-4;t=t<<3;
r=(int)(5.0+sqrt(25+t))>>2;
s=(r*(r-2)<<1)-r+4;
z=(r<<1)-1;
o=N-s;
A=z-abs(o-z+1);
t=N-2;t=t<<3;
r=(int)(3.0+sqrt(9+t))>>2;
s=((r*(r-1))<<1)-r+2;
z=r<<1;
o=N-s;
B=z-abs(o-z+1);
/*
cout<<"N="<<N<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"ra="<<ra<<" ";
cout<<"sa="<<sa<<" ";
cout<<"za="<<za<<" ";
cout<<"oa="<<oa<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"rb="<<rb<<" ";
cout<<"sb="<<sb<<" ";
cout<<"zb="<<zb<<" ";
cout<<"ob="<<ob<<" ";
cout<<endl;
*/
cout<<"TERM "<<N<<" IS "<<A<<"/"<<B<<endl;
};
return 0;
}
Monday, March 5, 2012
My solution of UVA 10054 - The Necklace
10054 - The Necklace
Background:
Euler : Visited every Edges.
== every nodes are connected and have even connected edges. (Euler Cycle)
* until all edges are visited.
** G MUST always be still an Euler cycle.
Solution to 10054
- Node: color (1-50), Edge:Beam (50,50)
- Build a graph matrix = long G[51][51]
- Build a degree array dgr[51]: dgr[i]=sum of connected edges.
Task 1 - Check connected:
- use array int p[51];
- int find(int x)
Task 2 - Check even edges
- If any dgr[i]%2!=0, return false;
Task 3 - Build Euler
for(i=0;!dgr[i];i++); // find the least node with dgr[i]>0
dfs(i);
int dfs(int u)
{
int v;
for(v=1;v<=50;v++)
if(G[u][v])
{
G[u][v]--;
dfs(v);
cout<<v<<" "<<u<<endl;
}
}
Background:
Euler : Visited every Edges.
== every nodes are connected and have even connected edges. (Euler Cycle)
Fleury's Algorithm - Find the Euler Cycle.
== Build a new graph by obtaining edge 1 by 1 from the original Euler graph (G).* until all edges are visited.
** G MUST always be still an Euler cycle.
Solution to 10054
- Node: color (1-50), Edge:Beam (50,50)
- Build a graph matrix = long G[51][51]
- Build a degree array dgr[51]: dgr[i]=sum of connected edges.
Task 1 - Check connected:
- use array int p[51];
- int find(int x)
{
return (p[x]==x)?x:find(p[x]);
}
- Verify if all node pair (u,v) are connected?
if(find(u)==find(v))?
- If 2 nodes have edge, connect them:
p[find(u)]=find(v);
Task 2 - Check even edges
- If any dgr[i]%2!=0, return false;
Task 3 - Build Euler
for(i=0;!dgr[i];i++); // find the least node with dgr[i]>0
dfs(i);
int dfs(int u)
{
int v;
for(v=1;v<=50;v++)
if(G[u][v])
{
G[u][v]--;
G[v][u]--;
dfs(v);
cout<<v<<" "<<u<<endl;
}
}
My solution of UVA 10305 Ordering Tasks
10305 - Ordering Tasks
Trace the graph with given edges direction.
- repeatly count all node in-degree, find the local root (in-degree=0), print it and remove its in-edge(in-arrow).
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define sz(k) (int)(k).size()
#define tr(c,i) for(typeof((c).begin()) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); i++)
#define forr(i,r) for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define drep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define pb push_back
#define nl(c) c<<endl;
#define db(cout,c) tr(c,it){cout<<" "<<*it;};nl(cout);
#define inf32 (int)(1<<31-1)
#define inf64 (int)(1<<63-1)
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int N,M;
while(cin>>N>>M)
{
if(N==0)break;
long A[M],B[M];
forr(i,M)
cin>>A[i]>>B[i];
long cnt=0;
bool P[N+1];
rep(i,0,N){P[i]=false;}
while(true)
{
long C[N+1];
rep(i,0,N){C[i]=0;}
forr(i,M)
if(B[i]>0)
C[B[i]]++;
rep(i,1,N)
if(!P[i])
if(C[i]==0){
forr(j,M)if(A[j]==i)B[j]=-1;
cout<<i<<" ";
P[i]=true;
cnt++;
};
if(cnt>=N)break;
}
cout<<endl;
/* vector< pair<long,long> > T;
forr(i,M){
pair< long,long> pp;
cin>>pp.second>>pp.first;
T.push_back(pp);
}
sort(T.begin(),T.end());
tr(T,ti)cout<<(*ti).first<<endl;
*/
}
return 0;
}
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)